Microsoft APIs beyond ODBC
Question: How does Microsoft ODBC differ from (ADO) Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects?
Microsoft ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) and Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects (ADO) are both technologies used to connect to databases and retrieve data in Microsoft Windows environments. However, there are several key differences between the two technologies:
Overall, the main difference between ODBC and ADO is their level of abstraction and the types of data sources they are designed to work with. ODBC provides a lower-level interface for working with relational databases, while ADO provides a higher-level abstraction for working with a variety of data sources.
- Object model: ADO is an object-oriented interface, while ODBC is a lower-level API. ADO provides a higher-level abstraction for working with data, while ODBC provides a lower-level interface for accessing data.
- Data access: ADO is a general-purpose data access technology that supports a variety of data sources, including relational databases, XML, and text files. ODBC, on the other hand, is primarily designed for accessing relational databases.
- Performance: ODBC is typically faster than ADO because it is a lower-level API and provides more direct access to the database. However, ADO can be faster for certain types of data access, such as retrieving large amounts of data or working with disconnected datasets.
- Platform support: ODBC is a cross-platform technology that works on a variety of operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS. ADO, on the other hand, is primarily designed for use on Windows platforms.
- Language support: ADO is designed to work with a variety of programming languages, including Visual Basic, C++, and Java, while ODBC is primarily designed for use with C and C++.
Overall, the main difference between ODBC and ADO is their level of abstraction and the types of data sources they are designed to work with. ODBC provides a lower-level interface for working with relational databases, while ADO provides a higher-level abstraction for working with a variety of data sources.
Legacy Technologies from Microsoft
The
The Microsoft Universal Data Access (UDA) is a term that incorporates ODBC, RDS, ADO, and OLE DB. The (legacy) JDBC 2.0 API includes the UDA functionality, including SQL3 support. Each of the Microsoft technologies are designed to run on Windows operating systems, and they provide little if any support for other platforms.
- OLE (Object Linking and Embedding) DB,
- ADO (ActiveX Data Objects), and
- RDS (Remote Data Service)
The Microsoft Universal Data Access (UDA) is a term that incorporates ODBC, RDS, ADO, and OLE DB. The (legacy) JDBC 2.0 API includes the UDA functionality, including SQL3 support. Each of the Microsoft technologies are designed to run on Windows operating systems, and they provide little if any support for other platforms.
ODBC
The (ODBC) Microsoft Open Database Connectivity interface is a C programming language interface that makes it possible for applications to access data from a variety of database management systems (DBMSs).
ODBC is a low-level, high-performance interface that is designed specifically for
relational database management systems.
The ODBC interface allows maximum interoperability and an application can access data in diverse DBMSs through a single interface. In addition, that application will be independent of any DBMS from which it accesses data. Users of the application can add software components called drivers, which interface between an application and a specific DBMS.
The ODBC interface allows maximum interoperability and an application can access data in diverse DBMSs through a single interface. In addition, that application will be independent of any DBMS from which it accesses data. Users of the application can add software components called drivers, which interface between an application and a specific DBMS.
Microsoft Connectivity Technologies
ADO.NET is a high-level application-programming interface that is targeted at loosely coupled, n-tier,
internet-based applications that support disconnected access to data. It is a core component of the Microsoft .NET Framework.
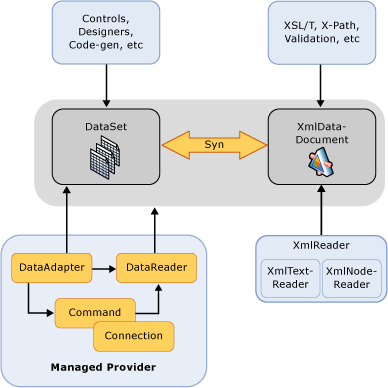
ADO.NET provides .NET-managed providers for connected access, and DataSets that read and write in XML for disconnected management of retrieved data and user interaction.
For more information about data providers in ADO.NET, see .NET Framework Data Providers.
The DataSet reads and writes XML, and the XMLDataDocument integrates relational and XML views. For more information about data sets, see ADO.NET DataSets.
The DataSet reads and writes XML, and the XMLDataDocument integrates relational and XML views. For more information about data sets, see ADO.NET DataSets.
RDS (Remote Data Service)
Remote Data Service (RDS) is a feature of ADO, with which you can move data from a server to a client application or Web page, manipulate the data on the client, and return updates to the server in a single round trip. Beginning with Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012, RDS server components are no longer included in the Windows operating system (see Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 Compatibility Cookbook for more detail). RDS client components will be removed in a future version of Windows. Avoid using this feature in new development work, and plan to modify applications that currently use this feature. Applications that use RDS should migrate to WCF Data Service.
Microsoft JDBC Driver for SQL Server
he Microsoft JDBC Driver for SQL Server is a Java database driver that provides connectivity to Microsoft SQL Server databases. Some of the key characteristics of the driver include:
Overall, the Microsoft JDBC Driver for SQL Server is a robust and high-performance JDBC driver that provides efficient connectivity to SQL Server databases, with support for a wide range of SQL Server features and cross-platform compatibility.
The Microsoft JDBC Driver for SQL Server is a Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) 4.0 compliant driver that provides robust data access to SQL Server databases. The JDBC driver can be installed on the Windows and UNIX operating systems.
- High-performance data access: The driver is optimized for high-performance data access to SQL Server databases, providing efficient query processing and optimized network communication.
- Support for SQL Server features: The driver supports a wide range of SQL Server features, including stored procedures, views, and triggers. It also supports the latest SQL Server versions and features, including Always On availability groups, Columnstore indexes, and Transparent Data Encryption (TDE).
- Easy installation and configuration: The driver can be easily installed and configured on a Java development environment, and it supports a variety of Java development environments, including Java SE, Java EE, and Spring.
- Cross-platform compatibility: The driver supports a variety of platforms, including Windows, Linux, and macOS, and can be used in a variety of Java-based applications.
- Secure connectivity: The driver provides secure connectivity to SQL Server databases through support for SSL/TLS encryption and integrated Windows authentication.
- Performance optimizations: The driver includes several performance optimizations, including connection pooling, batch updates, and result set caching, to improve performance and reduce network traffic.
Overall, the Microsoft JDBC Driver for SQL Server is a robust and high-performance JDBC driver that provides efficient connectivity to SQL Server databases, with support for a wide range of SQL Server features and cross-platform compatibility.
The Microsoft JDBC Driver for SQL Server is a Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) 4.0 compliant driver that provides robust data access to SQL Server databases. The JDBC driver can be installed on the Windows and UNIX operating systems.
Windows Communication Foundation
Windows Communication Foundation, which was code-named Indigo, is a technology that allows pieces of software to communicate with one another. There are many other such technologies, including the Component Object Model and Distributed Component Object Model, Remote Method Invocation, Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ), and WebSphere MQ. Each of those works well in a particular scenario, not so well in others, and is of no use at all in some cases. The Windows Communication Foundation is meant to work well in any circumstance in which a Microsoft .NET assembly must exchange data with any other software entity. In fact, the Windows Communication Foundation is meant to always be the very best option. Its performance is at least on par with that of any other alternative and is usually better; it offers at least as many features and probably several more. It is certainly always the easiest solution to program.
JDBC Metadata